What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing (QC) is a new computing model that follows the laws of quantum mechanics to control quantum information units for computing. Unlike traditional computing, quantum computing follows the laws of quantum mechanics and is a new computing model that can break through the bottleneck of traditional computing power. Quantum computers, as devices that perform quantum computing tasks, use quantum bits (qubits) as basic computing units. In quantum computing, based on the principle of quantum superposition, different states of quantum bits can be stored and processed simultaneously. The incredible and rapidly increasing power and capabilities of quantum computing are already changing the way we use computers to solve problems, analyze information, and protect data.

What is Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC)?
Post-Quantum Cryptography is a mathematical cryptographic system that can be implemented on existing computers and resist attacks from future quantum computers. Its algorithm is based on mathematical problems that are difficult to crack with quantum computing, such as lattice cryptography, multivariate polynomials, and coding theory. It can be compatible with existing systems through a hybrid encryption mechanism. Although it may take several years for a quantum computer to truly function, it is still possible to deal with the security threats of "harvest now, decrypt later", it requires the adoption of PQC algorithms now to protect important data from various current and future forms of attacks, whether using traditional computers or future quantum computers.

What are the PQC standards?
The US NIST released three PQC standards in August 2024:
(1) FIPS-203: It is based on Module Lattice-Based Key Encapsulation Mechanism (ML-KEM), which enables the generation of secure keys for data encryption (such as HTTPS). It is secure against quantum-enabled attacks. It includes ML-KEM-512, ML-KEM-768, and ML-KEM-1024.
(2) FIPS-204: A digital signature algorithm based on Module-Lattice (ML-DSA), which uses Fiat-Shamir with Aborts to resist quantum attacks. Its key and signature sizes are moderate, and the signature is fast, and the signature validation is even faster.
(3) FIPS-205: A hash-based digital signature algorithm (SLH-DSA) that uses HORST and W-OTS to resist quantum attacks and has the advantage of shorter public and private keys, although the signature is longer than ML-DSA.
ZoTrus PQC HTTPS Ecosystem Product Readiness Schedule
1
ZT Browser and ZoTrus Gateway support the ECC+MLKEM and SM2+MLKEM hybrid key encapsulation mechanism for HTTPS.
2025.12
2
ZoTrus CA creates ECC+MLDSA and SM2+MLDSA hybrid root CA certificates and sub-CA certificates to issue hybrid PQC SSL certificates.
2026.03
3
ZT Browser and ZoTrus Gateway support PQC hybrid algorithm SSL certificate, to realize adaptive PQC algorithm HTTPS encryption.
2026.09
4
ZoTrus CA creates pure PQC algorithm (MLDSA) root CA certificate and sub-CA certificates to issue pure PQC SSL certificates.
2026.12
5
ZT Browser and ZoTrus Gateway support pure PQC algorithm SSL certificate, to realize pure PQC algorithm HTTPS encryption.
2027.07
6
ZT Browser and ZoTrus Gateway support China PQC algorithm SSL certificate, to realize China PQC algorithm HTTPS encryption.
2028.12
7
ZoTrus has created full ecosystem of HTTPS PQC products, supporting China/Intl PQC algorithms, achieves seamless PQC migration.
2029.12
Tackle the upcoming two HTTPS revolutions in one go
- The technological revolution of "SSL certificate management from manual to automatic" must be completed before March 15, 2026
- The technological revolution of “HTTPS from traditional cryptography to quantum-resistant cryptography” must be completed before December 31, 2029
- The ultimate goal of the first technological revolution is to easily achieve the second technological revolution
- ZoTrus innovatively achieves a micro-transformation to complete the necessary technological transformation for two technological revolutions
- Since two technological revolutions are necessary, let’s complete them at once
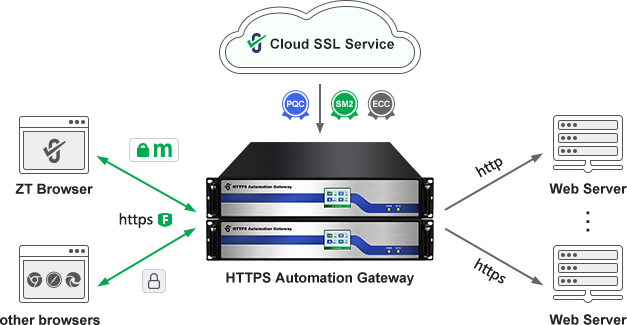
ZT Browser and ZoTrus Gateway support the ECC/SM2+PQC hybrid KEM
- ZT Browser and ZoTrus HTTPS Automation Gateway already support ECC+MLKEM768 hybrid key encapsulation mechanism to implement HTTPS encryption, and the website deploys ECC algorithm SSL certificate.
- ZT Browser and ZoTrus HTTPS Automation Gateway are planning to support SM2+MLKEM768 hybrid key encapsulation mechanism to implement SM2 algorithm HTTPS encryption in December 2025, and the website will deploy SM2 algorithm SSL certificate.
- ZoTrus Gateway automatically connects to ZoTrus Cloud SSL Service System to automatically apply for and deploy dual-algorithm (ECC+SM2) SSL certificates for websites, and adapts to four algorithms to implement HTTPS encryption: ECC algorithm, SM2 algorithm, ECC+PQC algorithm, SM2+PQC algorithm. ZT Browser uses the SM2+PQC algorithm, Google Chrome uses the ECC+PQC algorithm, other browsers that do not support the PQC algorithm use the ECC algorithm, and browsers that support SM2 algorithm use the SM2 algorithm.
- No modification, upgrade or cost on the user side, as long as the ZoTrus HTTPS Automation Gateway has been deployed.


ZoTrus CA creates ECC/SM2+PQC hybrid root CA certificates
- Offline use of ZoTrus HSM to generate hybrid algorithm (ECC384+MLDSA768) private key and self-signed root CA certificates, and generate hybrid algorithm (SM2+MLDSA768) private key and self-signed root CA certificates.
- In ZoTrus CA system, ZoTrus HSM is used to generate hybrid algorithm (ECC256+MLDSA768) and (SM2+MLDSA768) private keys and CSR files, and uses the two self-signed root CA to digitally sign the PQC hybrid algorithm sub-CA certificates, which is used to issue PQC hybrid algorithm (ECC256+MLDSA768) SSL certificates and (SM2+MLDSA768) SSL certificates respectively.
- Develop and deploy the ML-DSA algorithm certificate transparency log system to enable the PQC hybrid algorithm SSL certificate to support certificate transparency.
- This development and deployment work will be completed in March 2026.
ZT Browser and ZoTrus Gateway support PQC hybrid algorithm SSL certificates
- ZT Browser includes the two ZoTrus PQC hybrid algorithm root CA certificates and supports validation of PQC hybrid algorithm SSL certificates.
- ZoTrus HTTPS Automation Gateway supports PQC hybrid algorithm SSL certificates, and works with ZT Browser to implement PQC algorithm HTTPS encryption. The Gateway also automatically configures ECC/SM2/PQC hybrid algorithm SSL certificates to support 5 algorithms: ECC algorithm, SM2 algorithm, ECC+PQC algorithm, SM2+PQC algorithm, PQC algorithm.
- ZT Browser supports validation of ML-DSA algorithm certificate transparency log signature data to use the certificate transparency mechanism currently used by global SSL certificates.
- ZT Browser uses the PQC algorithm first to implement HTTPS encryption. Other browsers that do not support the PQC hybrid algorithm SSL certificate use other algorithms: ECC algorithm, SM2 algorithm, ECC+PQC algorithm, SM2+PQC algorithm.
- This development and deployment work will be completed in September 2026.


ZoTrus CA creates pure PQC algorithm root CA certificates
- Offline use of ZoTrus HSM to generate pure PQC algorithm (MLDSA-768) private key and self-signed root CA certificate.
- In ZoTrus CA system, ZoTrus HSM is used to generate pure PQC algorithm (MLDSA-768) private key and CSR file, and use the self-signed root CA certificate to digitally sign the pure PQC algorithm sub-CA certificates, which is used to issue pure PQC algorithm (MLDSA-768) SSL certificates.
- Submit the pure PQC algorithm SSL certificate to the ML-DSA algorithm certificate transparency log system to make the pure PQC algorithm SSL certificate support certificate transparency.
- This development and deployment work will be completed in December 2026.
ZT Browser and ZoTrus Gateway support pure PQC algorithm SSL certificates
- ZT Browser includes the ZoTrus pure PQC algorithm root CA certificates and supports validation of pure PQC algorithm SSL certificates.
- ZoTrus HTTPS Automation Gateway supports pure PQC algorithm SSL certificates, and works with ZT Browser to implement PQC algorithm HTTPS encryption. The Gateway also automatically configures ECC/SM2/PQC hybrid/pure PQC algorithm SSL certificates to support 5 algorithms: ECC algorithm, SM2 algorithm, ECC+PQC algorithm, SM2+PQC algorithm, PQC algorithm.
- ZT Browser supports validation of ML-DSA algorithm certificate transparency log signature data to use the certificate transparency mechanism currently used by global SSL certificates.
- ZT Browser uses the PQC algorithm first to implement HTTPS encryption. Other browsers that do not support the PQC algorithm SSL certificate use other algorithms: ECC algorithm, SM2 algorithm, ECC+PQC algorithm, SM2+PQC algorithm.
- This development and deployment work will be completed in July 2027.


ZT Browser and ZoTrus Gateway support China PQC algorithm SSL certificates
- This plan depends on when China will release the PQC algorithm cryptographic industry standard, which is expected to be released in 2027 or 2028.
- ZoTrus CA system generates China PQC algorithm root CA certificates and sub-CA certificate for issuing China PQC algorithm SSL certificates.
- ZT Browser includes the ZoTrus China PQC algorithm root CA certificates and supports validation of China PQC algorithm SSL certificates.
- ZoTrus HTTPS Automation Gateway supports China PQC algorithm SSL certificates, and works with ZT Browser to implement China PQC algorithm HTTPS encryption. The Gateway also automatically configures ECC/SM2/PQC hybrid/Intl’ PQC/China PQC algorithm SSL certificates to support 6 algorithms: ECC algorithm, SM2 algorithm, ECC+PQC algorithm, SM2+PQC algorithm, Intl’ PQC algorithm, China PQC algorithm.
- Setup China PQC algorithm certificate transparency log system, ZT Browser supports validation of China PQC algorithm certificate transparency log signature data.
- ZT Browser uses the China PQC algorithm first to implement HTTPS encryption. Other browsers that do not support the China PQC algorithm SSL certificate use other algorithms: ECC algorithm, SM2 algorithm, ECC+PQC algorithm, SM2+PQC algorithm, Intl PQC algorithm.
- This development and deployment work will be completed in December 2028.
ZoTrus creates a full ecosystem of HTTPS PQC algorithm products to achieve seamless PQC migration
- HTTPS PQC algorithm full ecosystem products: ZT Browser, ZoTrus HTTPS Automation Gateway, ZoTrus PQC HSM, ZoTrus PQC CA System, ZoTrus PQC Certificate Automation Service System, ZoTrus PQC Certificate Transparent Log.
- ZT Browser support the PQC algorithms are completely free, just need to update to the latest version. It supports Windows, UOS and KylinOS, Android, IOS, HarmonyOS and other operating systems.
- ZoTrus HTTPS Automation Gateway will automatically upgrade to support the PQC algorithms for free. Once deployed, the user can seamlessly and automatically complete the PQC migration without additional upgrade and transformation costs.
- The HTTPS PQC algorithm full-ecosystem products exclusively created by ZoTrus Technology have completely independent intellectual property, and it is a self-contained system that fully supports the PQC algorithm. It is the first choice for customers to calmly move into the PQC era.