Why must code signing have timestamps?January 6 , 2026
Please indicate when reprinting: Reprinted from ZoTrus CEO Blog)
To ensure Windows system security, Microsoft employs a zero-trust policy, zero trust to software without digital signatures; all software must have a digital signature. This article explains why code signatures must include a timestamp. First, let's look at a screenshot of the digital signature of an "old" software — Firefox 2011 version:
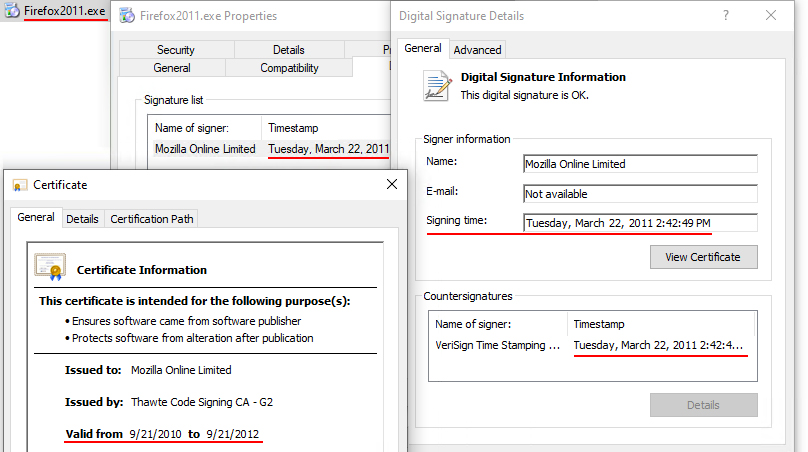
This software was signed on March 22, 2011, and its code signing certificate expired on September 21, 2012. However, its digital signature remains valid more than a decade later, and it can still run, install, and display the signer's information. This is the function of a timestamp. Without a timestamp, although the software has a digital signature, the digital signature becomes invalid once the code signing certificate used to sign the code expires. Currently, code signing certificates have a maximum validity period of 3 years, and from March 1st, the validity period will be one year. However, the lifecycle of a software is generally longer than one year, especially for some utility software or device drivers, like the software mentioned above, which is more than 14 years old today.
A timestamp is also a type of digital signature. It requires a system that provides timestamp signing service, called a "timestamp system" or "timestamp server" and of course, with a timestamp signing certificate. The working principle is illustrated in the diagram below. The user uses a code signing tool to generate digest data for the file to be signed and submits this data to the timestamp server to request a signature. The timestamp server signs the digest data and a date/time record from an authoritative time source, generating timestamp signature data which is returned to the signing tool. The signing tool then writes this timestamp data into the file to be signed, thus completing the timestamp signing.
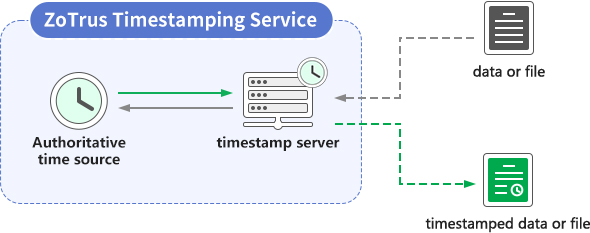
ZoTrus code signing cloud service automatically attaches a globally trusted timestamp signature to each signature, ensuring that the digital signature of the code remains valid even after the code signing certificate expires, thus guaranteeing the security and trustworthiness of the software throughout its entire lifecycle.